An Introduction to Generative AI Concepts
Understand the key Generative (Gen) AI concepts to take advantage of its amazing solutions and potential in business applications.
Gen AI for business, in simple terms, is like having a smart tool that can create things on its own.
Picture yourself as a chef with a twist—instead of relying on fixed recipes, envision having a magical kitchen helper capable of conjuring up innovative new recipes just for you.
In the business world, Gen AI can generate all sorts of useful stuff, like writing reports, making art, or even coming up with ideas for new products.
It's like having a creative assistant that helps you be more productive and innovative.
Today we will cover:
The Economic Impact of Gen AI
The Key Gen AI Concepts
The main characteristic of Gen AI: the Foundation Models (FMs)
Benefits of Gen AI over Predictive Machine Learning (ML)
Most Common Gen AI for Business
Let's dive in! 🤿
The economic impact of Gen AI
In accordance with McKinsey's report "The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier."
All workers productivity enabled by generative AI could be incremented by 35 to 70% ($6.1 to $7.9 trillion annually).
Automation potential will increase mainly in the areas of Decision Making and Collaboration from 24.5 to 58.5 % increase of productivity applying expertise to decision making, planning and creation of tasks.
As Gen AI continues its rapid evolution, we anticipate transformative changes across numerous industries, ushering in shifts in job demands and creating new dynamics in the workforce.
The Key Gen AI Concepts
As per below picture, Gen AI is a field within AI:
The term “Generative” comes from the concept that the AI systems will generate new data or content by emulating the data of a training set instead of analysing or processing existing content. Hence, in simple terms:
Generative AI is the “ability of artificial intelligence models to create new, original content and artifacts such as text, code, images, video, and more, that are new and unique”
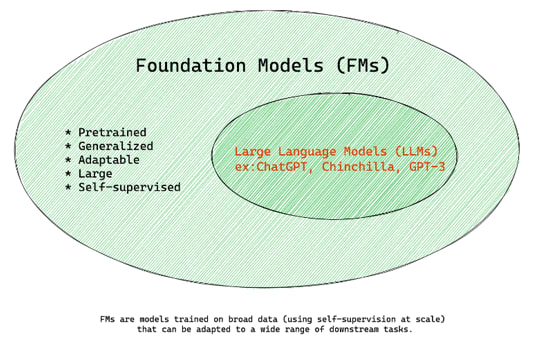
The Main characteristic of Gen AI: the Foundation Models (FMs)
At the core of the Gen AI we have the FMs that are trained on broad data using self-supervision and can be adapted to a wide range of downstream tasks.
One prominent subtype of Foundation Models is Large Language Models (LLMs), which include well-known entities like ChatGPT, Claude, Llama, and more.
LLMs showcase the capability of FMs to understand and generate diverse content, spanning text, code, images, video, and beyond.
In essence, Foundation Models serve as the bedrock, equipped with the ability to grasp intricate patterns, structures, and variations from extensive data. For instance, training a model on a dataset containing dog images enables it to discern the defining features of a dog and subsequently generate novel images embodying those characteristics. This adaptability and versatility make Foundation Models a cornerstone in the realm of Generative AI.
Benefits of Gen AI over Predictive Machine Learning (ML)
While Predictive ML, relying on Supervised Learning, presents challenges due to its difficulty, slow pace, and high cost, requiring substantial human effort and data labeling,
Gen AI is using self-supervised learning and:
the effort is made by the computer
requires little data labelling
it’s an efficient automation
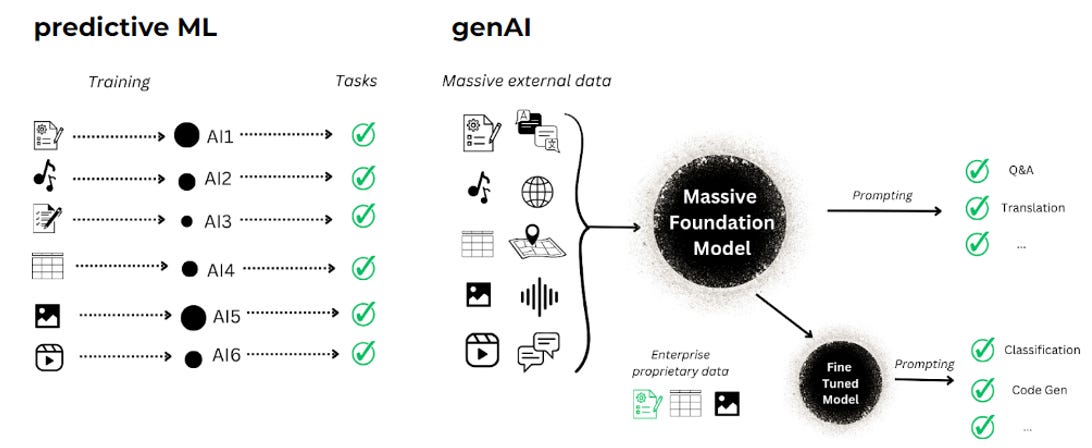
The visual representation below illustrates these differences.
In Predictive ML, each use case demands specific models and task-specific training, leading to significant human-supervised training efforts.
In contrast, Gen AI employs a Massive Foundation multi-tasking Model that adapts with minimal or no training, processing extensive external data. Through prompting, we can instruct the model for specific tasks.
Moreover, employing various techniques allows the model to be Fine-Tuned, enabling it to process proprietary enterprise data for superior and customized results.
Most Common Gen AI for Business
Gen AI applied for business becomes a powerful tool that can be applied to various sectors. The applications below showcase the potential to revolutionise the different industries.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Create a chatbot or question-answering feature.
i.e.: Building a Q&A resource Customer service assistance
Summarisation: Condenses textual information into concise summaries
i.e.: Conversation summaries Meeting transcripts
Content Generation: Generate text content for a specific purpose.
i.e.: Marketing campaigns; Job descriptions; Blog posts and articles, Email drafting support
Named Entity Recognition: Identify and extract essential information from unstructured text.
i.e.: Audit acceleration
Insight Extraction: Analyse existing unstructured text content to surface insights in specialized domain areas.
i.e.: Medical diagnosis support user research findings.
Classification: Read and classify written input with as few as zero examples.
i.e.: Sorting of customer complaints; Sentiment analysis.
Conclusions
Generative AI represents a new frontier for business productivity - one that promises to augment human creativity on a massive scale.
This quick overview covered what makes it distinct from previous AI, how foundation models work, its array of business uses cases, as well as the enormous projected economic impact.
While workforce disruption remains a valid concern, carefully leveraging generative AI's potential also presents an opportunity to propel dramatic gains.
As with any new technology, mindful governance and ethical considerations will be paramount.
By continuing to track developments, business leaders across sectors can capitalize on this transformational AI capability.
Disclaimer: The information provided in the newsletter and related resources is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional advice, and any actions taken based on the content are at the reader's discretion.