Aerospace Human Factors and AI [part 3/6]
AI's positive Impact on Aviation Human Factors.
In my article “Aerospace Human Factors and AI [part 2/6]” I introduced the fundamentals of Aviation Human Factors and the Dirty Dozen.
Despite being twelve common contributors to human error, typically common in the area of aircraft maintenance, we could argue that can be applied to other areas even industries.
These contributing factors, among others, can present risks that if not mitigated could line up ending in an error that could cause and incident or an accident.
Could Artificial Intelligence applied in business processes contribute in Human Factors mitigation maintaining airworthiness and safety?
This is the third article of the 6 series about Human Factors (HF) and AI, which is focused particularly on how AI can positively impact HF.
Part 1 - Introduction to Aviation Human Factors (HF)
Part 2 - The Relationship Between Human-Centred AI (HCAI) and Aviation Human Factors
Part 3 - AI's positive Impact on Aviation Human Factors
Part 4 - Emerging Human Factors Challenges Due to AI Adoption in Aviation
Part 5 - Understanding EASA's Building Block #3: A Deep Dive into Regulatory Compliance
Part 6 - Future Directions and Integration Strategies for HF and AI in Aviation
Today’s focus is:
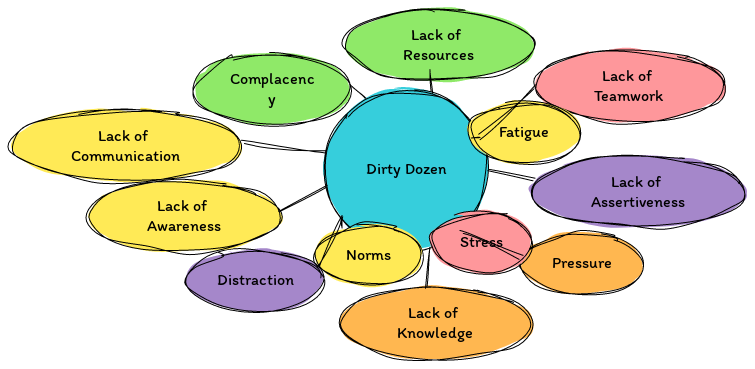
AI's Role in addressing the Dirty Dozen
AI’s impact on Organisational Culture and Leadership
Conclusions
Let’s dive in! 🤿
AI's Role in addressing the Dirty Dozen
Let’s explore how AI-enhanced tools could support mitigating each of the 12 contributing factors in operational environments:
Lack of Communication: Miscommunications in intentions, instructions, and changes can lead to serious errors. AI can enhance communication through:
Automated Alerts and Notifications: Automating the distribution of crucial information ensures all team members receive updates about schedules, changes, and safety notices in real time.
Enhanced Collaboration Tools: AI-driven platforms can synchronise team efforts, providing environments where communication is seamless and well-documented.
Language Translation: Real-time translation capabilities can bridge language barriers within globally diverse teams.
Voice-Enabled Assistants: These assistants facilitate hands-free communication, allowing technicians to exchange information without interruption.
Complacency: Complacency involves a sense of self-satisfaction with unawareness of potential dangers. AI combats this with:
Continuous Monitoring: AI systems monitor performance and protocol adherence, identifying deviations or shortcuts.
Alert Systems: AI sets operational thresholds and alerts personnel when routine checks are missed or standards are not met.
Predictive Maintenance: By predicting potential failures, AI keeps maintenance teams proactive, not just reactive.
Performance Feedback: Providing real-time feedback helps maintain high standards and counteract complacency.
Lack of Knowledge: Errors can stem from insufficient training or incomplete knowledge. AI addresses this through:
Personalised Learning: Tailoring training programs to individual technician needs, identifying and addressing knowledge gaps.
On-the-Job Training Tools: Augmented reality and virtual reality powered by AI simulate realistic maintenance scenarios for hands-on experience without associated risks.
Real-Time Assistance: AI support systems offer instant access to manuals, schematics, and expert advice, reducing downtime and enhancing task accuracy.
Knowledge Management: AI organises and retrieves vast data amounts, ensuring documentation and procedures are current and accessible.
Distraction: Distractions can lead to errors or incomplete tasks. AI mitigates distractions by:
Focused Task Alerts: Monitoring task performance and issuing alerts to refocus attention when needed.
Environmental Monitoring: Assessing the environment for potential distractions and adjusting settings or alerting the user to reduce these distractions.
Behavioural Analysis: Analysing predistraction behaviours to predict and preemptively address distractions.
Lack of Teamwork: Poor teamwork can result in miscommunications and errors. AI enhances teamwork with:
Team Performance Analytics: Analysing team interactions and performance to identify improvement areas.
Communication Facilitation: Ensuring seamless interaction among team members.
Role Optimisation: Assigning roles based on individual strengths and weaknesses to optimise team dynamics.
Fatigue: Physical or mental exhaustion can impair performance. AI helps manage fatigue by:
Fatigue Prediction: Analysing work schedules and physiological data to predict and monitor fatigue levels, recommending optimal work-rest cycles.
Smart Scheduling: Optimising shifts based on fatigue levels and workload to ensure well-rested, alert employees.
Lack of Resources: A shortage of tools, equipment, or information can lead to mistakes. AI optimises resource use by:
Resource Optimisation: Forecasting needs and scheduling resources efficiently.
Inventory Management: Managing inventory in real-time, predicting parts and tools needs, and automating supply orders.
Pressure: Urgency, whether real or perceived, can lead to rushed decisions and errors. AI alleviates pressure by:
Workload Management: Assessing and adjusting workloads and deadlines in real-time.
Decision Support Systems: Providing fast, data-driven decision support to alleviate pressure during critical operations.
Lack of Assertiveness: Failure to voice concerns can lead to unsafe or incorrect actions. AI encourages assertiveness with:
Virtual Training Simulations: Providing safe environments to practice assertiveness.
Feedback Systems: Offering objective, real-time performance feedback to encourage proactive communication.
Stress: Psychological pressures can affect performance and decision-making. AI supports stress management through:
Stress Detection Systems: Monitoring stress levels and providing management recommendations.
Workload Management: Assessing and adjusting workloads and deadlines in real-time.
Lack of Awareness: A failure to recognise consequences or lack of attention to detail can be disastrous. AI enhances awareness by:
Enhanced Monitoring: Monitoring both operational environments and human performance, providing real-time alerts.
Predictive Alerts: Alerting staff about potential consequences of their actions or overlooked details.
Norms: Detrimental unwritten rules or habits can evolve into standard practices. AI challenges these norms by:
Behavioural Analysis: Identifying and suggesting changes to counterproductive norms.
Cultural Change Initiatives: Using AI-driven insights to drive initiatives aimed at changing harmful organisational behaviours.
AI’s impact on Organisational Culture and Leadership
Leaders can also use AI to foster a culture of safety and continuous improvement and to assist in decision-making processes.
AI can transform organisational culture and leadership by:
Enhancing Decision-Making:
Provides data-driven insights for informed decisions.
Improves strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Improving Transparency:
Automates and documents processes for greater transparency.
Builds trust by ensuring compliance with regulations and ethical standards.
Personalising Employee Experiences:
Tailors HR processes to individual employee needs.
Identifies potential leaders based on performance data.
Fostering Innovation:
Automates routine tasks, freeing up time for creative initiatives.
Encourages a culture of innovation.
Enhancing Communication:
Streamlines internal communication across departments.
Provides real-time language translation to support global operations.
Conclusions
As I conclude this part of our series on Aerospace Human Factors and AI, I am optimistic regards the transformative role that AI can play not only in aviation but across various industries contributing to a safer, more efficient environment where our teams can excel.
This inspires and reassures me about our path forward.
However, as any emerging technology it might bring as well challenges and create new risks. This is why in the next article I will focus on the emerging Human Factors challenges due to AI adoption in Aviation.
Stay tuned to continue exploring.
That’s all for today.
See you next week. 👋
References
Anderson, J. (2023). AI Business Strategy - QuickStart Solution (With 7 Easy Strategies). Printed by Amazon.
Banc K. (2023). The CEO’s Guide To Generative AI. Printed by Amazon. Printed by Amazon.
Patel, David A. (2023). Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners. Printed by Amazon.
IBM (2023). The CEO’s Guide to Generative AI. IBM Corporation.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this newsletter and related resources is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It reflects both researched facts and my personal views. It does not constitute professional advice. Any actions taken based on the content of this newsletter are at the reader's discretion.